How Will the Future of Plastic Pyrolysis Shape the Global Waste Management Landscape?
- lee784287
- 2024年3月5日
- 讀畢需時 2 分鐘
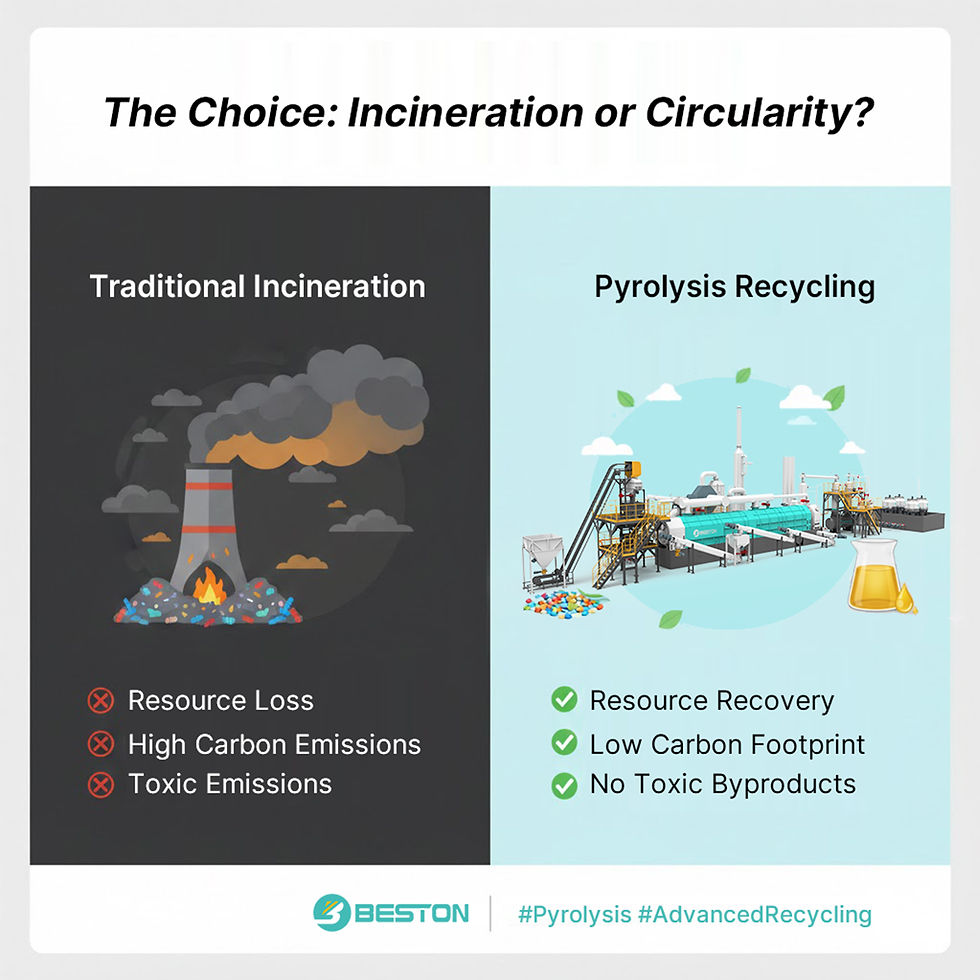
Plastic pyrolysis entails the thermal decomposition of plastic waste in the absence of oxygen, leading to the generation of pyrolysis oil, gas, and char. Unlike traditional recycling methods, which often result in downcycling or incineration, plastic pyrolysis offers a closed-loop solution that enables the recovery of high-value products from end-of-life plastics.
The advent of plastic pyrolysis plants heralds a paradigm shift in waste management practices. These facilities utilize advanced pyrolysis reactors and catalytic systems to convert a wide range of plastic materials, including polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene, into valuable fuels and chemical feedstocks. By harnessing the principles of circularity and resource efficiency, plastic pyrolysis mitigates the environmental impacts of plastic waste while creating economic opportunities.

One of the key advantages of plastic pyrolysis machine lies in its ability to address the challenges associated with plastic recycling. Unlike mechanical recycling, which is often limited by factors such as contamination and polymer degradation, plastic pyrolysis can process mixed or contaminated plastic streams, thus expanding the scope of recoverable materials. This versatility not only enhances the efficiency of waste management systems but also reduces reliance on virgin fossil fuels for the production of plastics and fuels.
Furthermore, plastic pyrolysis holds promise for decentralized waste management solutions, particularly in regions lacking robust recycling infrastructure. By enabling on-site or community-scale processing of plastic waste, plastic pyrolysis plants empower communities to take control of their waste streams while reducing transportation and logistics costs associated with traditional waste disposal methods.
The implications of plastic pyrolysis extend far beyond waste management; they encompass broader socio-economic and environmental considerations. By diverting plastic waste from landfills and incinerators, plastic pyrolysis mitigates greenhouse gas emissions, reduces pressure on natural ecosystems, and mitigates the risks of plastic pollution to marine and terrestrial environments. Moreover, the production of pyrolysis oil and gas offers a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, thus contributing to energy security and climate change mitigation efforts.
However, the widespread adoption of plastic pyrolysis faces several challenges, ranging from technological constraints to market dynamics and regulatory frameworks. The scalability and cost-effectiveness of plastic pyrolysis plants depend on factors such as feedstock availability, process efficiency, and market demand for recovered products. Additionally, ensuring environmental sustainability and social equity requires proactive measures to address concerns related to emissions, waste management practices, and community engagement.


留言