From Waste to Energy: Pyrolysis Plant Solutions for Diverse Feedstocks
- lee784287
- 1月16日
- 讀畢需時 2 分鐘
The conversion of waste into usable energy has become a central objective for industries facing rising disposal costs and tightening environmental regulations. Among the available technologies, pyrolysis has emerged as a robust thermochemical pathway capable of processing heterogeneous feedstocks while recovering energy-dense outputs. Its value lies not only in waste reduction, but in the controlled transformation of discarded materials into oil, gas, and solid carbon products.
Technical Principle of Pyrolysis Conversion
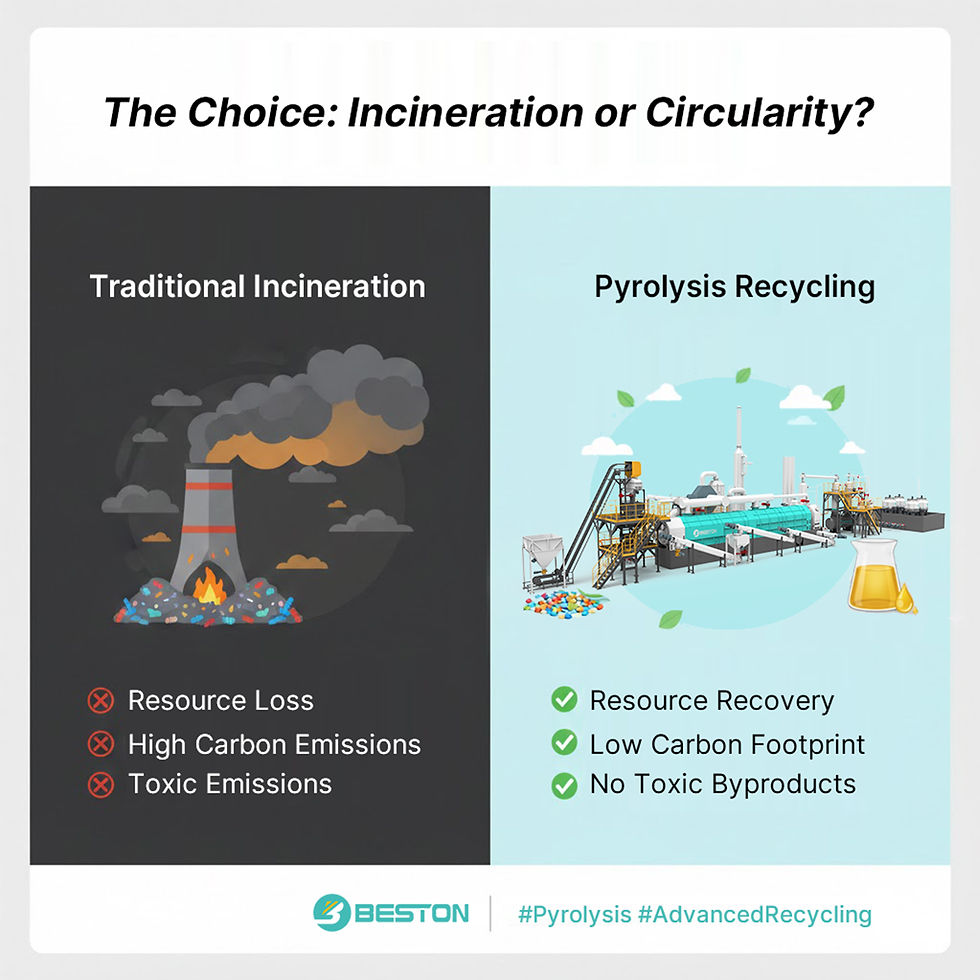
Pyrolysis operates under oxygen-deficient conditions, applying elevated temperatures to decompose complex organic matter. Unlike incineration, it avoids full oxidation. This distinction allows higher energy retention and improved control over product distribution. Short-chain hydrocarbons are released as pyrolysis gas, condensable vapors form liquid oil, and the remaining fixed carbon becomes char. Each fraction has industrial relevance, depending on the feedstock composition and process configuration, which are the key factors that influence pyrolysis plant for sale.

Feedstock Diversity and Process Adaptability
One of the defining advantages of pyrolysis technology is feedstock tolerance. Waste tires, plastic residues, oil sludge, biomass, and mixed industrial waste can all be processed with appropriate pre-treatment and reactor tuning. Particle size, moisture content, and volatile ratio directly influence residence time and heat transfer efficiency. Modern systems employ modular reactors and adaptive temperature zoning to stabilize output quality despite fluctuating input characteristics.
Energy Recovery and System Integration
Energy recovery is central to economic viability. Non-condensable gas generated during pyrolysis is typically recirculated as a supplemental fuel, reducing external energy demand. In integrated layouts, recovered heat supports drying, material handling, or downstream processing. This internal energy balancing improves thermal efficiency and lowers operational expenditure, particularly for continuous-feed industrial plants.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
From an environmental perspective, pyrolysis offers measurable advantages. It minimizes landfill dependency, reduces uncontrolled emissions, and enables carbon containment in solid char. Emission control units, including quench towers and multi-stage filtration, are essential to meet regulatory thresholds. When properly engineered, pyrolysis systems align with circular economy frameworks by converting problematic waste streams into secondary resources.
Commercial Deployment and Market Demand
Global interest in waste-to-energy infrastructure continues to expand, driven by policy incentives and resource scarcity. Industrial operators evaluating a pyrolysis plant for sale typically prioritize feedstock compatibility, automation level, and long-term maintenance requirements. Capital expenditure is often offset by multiple revenue channels, including recovered oil, fuel gas utilization, and carbon-based byproducts.
Long-Term Operational Value
Beyond immediate waste disposal, pyrolysis plants deliver strategic value through resource independence and process stability. Their scalability allows deployment across varying production capacities, from regional waste hubs to on-site industrial applications. With advancements in reactor materials and digital process control, operational reliability has improved significantly over earlier generations of equipment.
Pyrolysis plant solutions represent a pragmatic convergence of waste management and energy recovery. By accommodating diverse feedstocks and delivering consistent outputs, they provide industries with a technically mature pathway to convert waste liabilities into functional energy assets.

留言