Pyrolysis Plant Contribution to Carbon Reduction Strategies
- lee784287
- 2025年9月2日
- 讀畢需時 3 分鐘
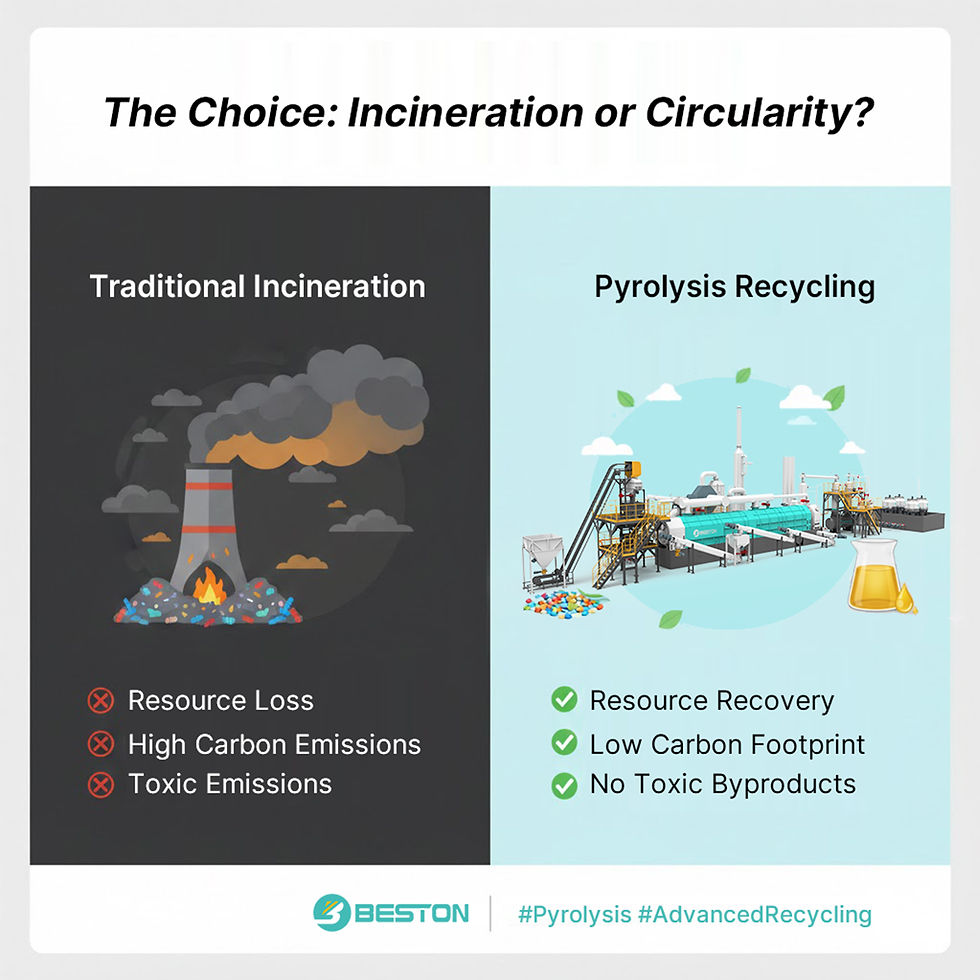
The global shift toward carbon mitigation has accelerated the adoption of advanced waste-to-energy technologies. Among them, the pyrolysis plant has emerged as a significant instrument in reducing carbon intensity across industrial sectors. By converting end-of-life materials such as plastics, rubber, and biomass into reusable outputs, these facilities not only diminish greenhouse gas emissions but also establish a pathway for circular resource utilization. The process transforms problematic residues into valuable commodities, aligning with both climate commitments and economic imperatives.
Conversion of Waste into Energy Resources
At the core of pyrolysis technology lies the principle of thermochemical decomposition under an oxygen-deprived atmosphere. This process prevents uncontrolled combustion and minimizes direct CO₂ discharge. Instead, it produces synthetic fuel oil, syngas, and biochar. Each output provides a replacement for fossil-derived alternatives, leading to measurable reductions in carbon footprints. A plastic to oil machine for sale, for example, directly substitutes virgin petroleum extraction by recovering usable liquid fuel from discarded polymers. This intervention avoids emissions generated during crude oil refining and reduces the environmental load associated with landfill accumulation.

Reduction of Methane and Leachate Hazards
Landfilling remains one of the largest contributors to methane, a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide. Pyrolysis interrupts this cycle by diverting waste streams away from conventional disposal routes. Instead of decomposing anaerobically over decades, materials are transformed in a controlled chamber within hours. Furthermore, pyrolysis prevents the leachate hazards common to unmanaged landfills, thereby minimizing indirect carbon-related consequences associated with groundwater contamination and subsequent remediation requirements.
Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
The by-products of pyrolysis offer synergies with renewable infrastructure. Syngas, a combustible mixture of hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide, can be harnessed to generate electricity or provide thermal energy for industrial operations. When paired with renewable power installations, such as solar or wind, pyrolysis enhances grid stability by supplying consistent baseload energy. This hybridization contributes to decarbonization strategies by offsetting reliance on coal or natural gas plants that typically provide backup power during demand peaks.
Industrial Decarbonization and Resource Security
Beyond energy substitution, pyrolysis plays a role in industrial decarbonization by delivering sustainable feedstocks. Recovered carbon black and char residues can be reintegrated into manufacturing chains, reducing dependency on resource-intensive virgin materials. The ability to utilize waste-derived products within tire, construction, or metallurgy sectors creates a closed-loop system with lower embodied carbon. Over time, this reduces industrial exposure to volatile fossil markets while reinforcing material security.
Contribution to Climate Policy Objectives
National and regional climate frameworks increasingly emphasize extended producer responsibility and low-carbon technology adoption. Pyrolysis plants align with these directives by providing tangible carbon abatement figures that can be integrated into sustainability reporting. Their deployment supports compliance with emission reduction targets under international accords, while simultaneously offering private investors attractive returns from resource recovery. The dual advantage of carbon reduction and profitability enhances their positioning as pivotal infrastructure in the low-carbon economy.
Conclusion
The pyrolysis plant represents more than a waste treatment option; it functions as a cornerstone in modern carbon reduction strategies. Through its capacity to displace fossil consumption, mitigate methane release, and integrate with renewable systems, it strengthens the foundation for long-term decarbonization. As market demand for sustainable technologies grows, investment in facilities such as the plastic to oil machine for sale underscores a pragmatic and effective response to the global imperative of carbon neutrality.


留言