The Economics of Biochar Equipment: Cost, ROI, and Market Demand
- lee784287
- 2025年7月29日
- 讀畢需時 2 分鐘
Biochar production is no longer confined to experimental setups or small-scale rural applications. Industrial deployment of biomass pyrolysis equipment is expanding rapidly as stakeholders recognize its potential in carbon sequestration, soil enhancement, and renewable energy systems. A thorough economic evaluation reveals that, beyond its environmental merit, biochar production offers viable financial returns when properly configured and deployed.
Capital Investment and Operational Costs
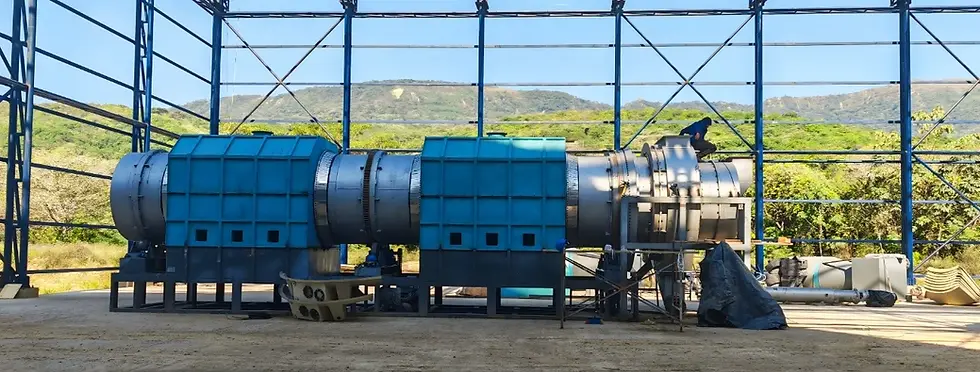
The upfront cost of biomass pyrolysis equipment varies significantly based on processing capacity, automation level, emission control systems, and regional manufacturing standards. Entry-level units with limited throughput and manual control may range from $30,000 to $80,000, while fully continuous systems with integrated gas cleaning and heat recovery mechanisms can exceed $500,000.
Operational expenses include feedstock acquisition or transport, labor, energy inputs for pre-drying (if necessary), maintenance, and post-processing (e.g., pelletizing or packaging). However, pyrolysis units that capture and utilize syngas or hot flue gas for internal heating can achieve energy self-sufficiency, reducing fuel costs considerably. In many cases, using agricultural or forestry residues as feedstock—often available at minimal cost—provides a favorable input-to-output value ratio.
Return on Investment (ROI)
The ROI for a biomass pyrolysis plant depends on throughput, local biomass availability, market access for biochar and co-products, and government incentives. Revenue streams typically include:
Biochar sales to agriculture, landscaping, and environmental remediation sectors.
Wood vinegar and tar as niche products in pest control or chemical industries.
Carbon credits, especially in regions aligned with voluntary or regulated carbon markets.
Under optimal conditions, medium-scale facilities can reach payback periods of 2 to 4 years. The inclusion of carbon offset revenue significantly accelerates ROI, particularly for projects certified under international methodologies such as Verra or Gold Standard.
Market Demand Dynamics
Market appetite for biochar is expanding, driven by soil degradation, rising fertilizer costs, and interest in regenerative agriculture. Demand is especially strong in sectors such as:
Viticulture and horticulture, where biochar enhances soil structure and water retention.
Livestock operations, which use biochar as a feed additive or manure management solution.
Green building, where biochar serves as a lightweight, insulating material.
Municipalities are also exploring biochar applications in urban forestry and stormwater filtration. These emerging uses indicate a broadening demand curve, which bolsters long-term market stability for pyrolysis-derived products.
Policy and Incentive Frameworks
Many jurisdictions now offer incentives that improve the financial outlook of biomass pyrolysis equipment. These include tax deductions for renewable energy systems, grants for waste valorization projects, and subsidies tied to sustainable agriculture. In carbon-regulated economies, monetizing sequestered carbon adds a substantial economic layer to the project’s value proposition.
Conclusion
The deployment of biomass pyrolysis equipment is economically viable when backed by strategic planning, robust market access, and integration with waste or agricultural ecosystems. With diversified revenue potential and increasing global demand for carbon-smart solutions, biochar production stands as a financially and environmentally sound investment in the evolving green economy.


留言