Utilizing Pyrolysis Plant Technology to Address Global Rubber Waste Crisis
- lee784287
- 2025年12月5日
- 讀畢需時 2 分鐘
The escalating accumulation of discarded rubber, particularly from end-of-life tyres, has become a critical environmental liability for many nations. Conventional disposal pathways—landfilling, open-air incineration, and uncontrolled dumping—exacerbate pollution, accelerate land scarcity, and release persistent toxins. In contrast, pyrolysis plant technology offers a thermochemical mechanism capable of converting rubber waste into marketable resources while mitigating ecological burdens. It delivers a continuous, process-driven approach that aligns with global demands for circular material management.
Converting Waste Rubber into Usable Commodities
Pyrolysis applies an oxygen-deprived heating regime to deconstruct long-chain polymeric structures found in rubber. This reaction yields three principal outputs: pyrolysis oil, carbon black, and non-condensable gas. Each fraction supports various industrial applications. Pyrolysis oil functions as a substitute feedstock for fuel blending or refining processes. Carbon black derived from tyre rubber exhibits utility in pigmenting, reinforcing compounds, and metallurgical operations. Meanwhile, the gas fraction can sustain internal heat supply, enabling partial energy self-sufficiency for the plant.
Process Reliability and Operational Architecture
A modern pyrolysis system integrates feeder units, thermal reactors, condensation assemblies, and emission control modules. Continuous-type reactors maintain stable thermal gradients and promote steady devolatilization of elastomeric material. Advanced heat-exchange configurations enhance calorific efficiency, while automated sealing mechanisms suppress oxygen ingress, which may influence cost of tyre pyrolysis plant. These attributes contribute to high throughput intensity and reduce operational downtime, a necessity for regions with significant tyre accumulation.

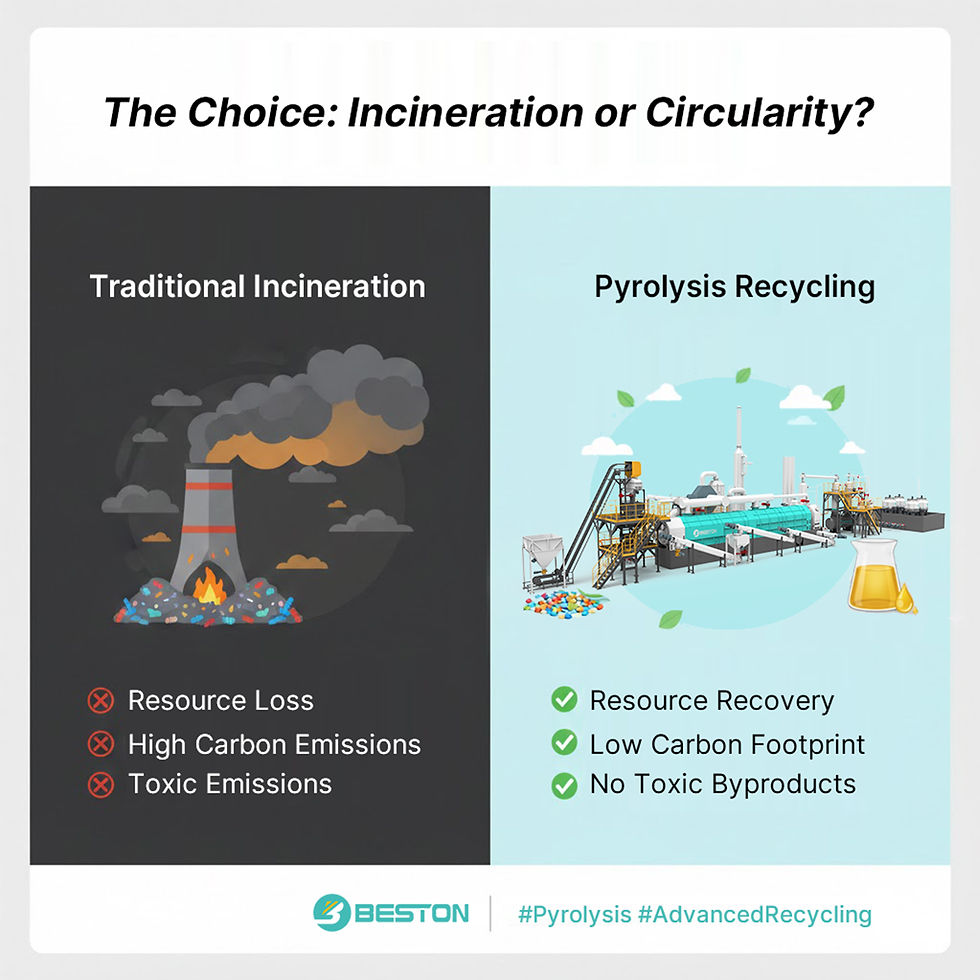
Environmental Advantages of Pyrolytic Treatment
Compared with incineration, pyrolysis minimizes atmospheric discharge of particulates and hazardous volatiles. Gas scrubbing assemblies and catalytic filtration curb acidic aerosols, thereby maintaining compliance with stringent air quality protocols. The method also lessens reliance on virgin fossil resources by supplying oil and carbon derivatives extracted from waste. Such displacement of primary extraction reduces associated greenhouse emissions and promotes resource recirculation at industrial scale.
Economic Considerations and Capital Outlay
The cost of tyre pyrolysis plant varies according to reactor capacity, level of automation, emission abatement configuration, and regional engineering standards. While initial investment is non-trivial, long-term economic advantages arise from saleable products, reduced waste management expenditures, and lower fuel procurement due to syngas reuse. Facilities designed with energy-recovery modules and refined condensation systems typically achieve improved yield metrics, enhancing revenue generation potential.
Role in Global Waste Governance
Many jurisdictions now seek scalable treatments that complement national waste-diversion policies. Pyrolysis plants provide a localized mechanism for diverting tyre stockpiles from landfills and unauthorized dumping sites. As international frameworks intensify scrutiny on waste exportation and improper handling, pyrolytic conversion offers a domestically anchored solution capable of meeting regulatory, environmental, and industrial expectations. The reliability of the technology positions it as a long-term component of sustainable rubber waste management strategy.


留言